7 Fascinating Facts About Heat Sink Technology You Need to Know
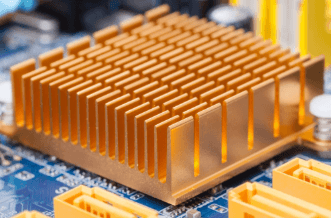
In today’s fast-moving world of technology, where speed matters a lot, there is a small but important part called the heat sink. Heat sinks quietly prevent devices like smartphones and supercomputers from overheating, ensuring they work well.
Discover seven fascinating facts about heat sink technology that explain how they work and why they’re important for innovation in many industries. Whether you enjoy technology or are just curious about how devices stay cool, you’ll find out why heat sinks are amazing!
Fascinating Fact #1: Heat Sinks Are Everywhere
Heat sinks are parts inside almost every electronic device, but you usually don’t see them. Their job is to remove heat from hot parts to keep devices cool. This keeps the device from getting too hot, which could cause problems or break it.
You can find heat sinks in many devices like laptops, LED lights, cars, smartphones, and medical machines, almost any electronic device needs a heat sink to stay cool. As technology advances, heat sinks have become smaller, lighter, and better designed to fit into tight spaces while keeping devices cool.
So, heat sinks quietly work behind the scenes in almost all our devices, helping them run safely and smoothly.
Fascinating Fact #2: Material Matters: Why Aluminum and Copper Dominate
Aluminum and copper dominate the world of heat sinks because they strike the perfect balance between thermal performance, cost, and practicality.
1. Aluminum: The Lightweight Workhorse
Thermal Conductivity: Good (around 205 W/m·K)
Key Advantages:
- Lightweight – ideal for portable electronics like laptops and smartphones.
- Cost-effective – significantly cheaper than copper.
- Easy to machine and shape – supports complex heat sink designs (like fins or extrusions).
- Corrosion-resistant – especially when anodized.
Aluminum is the default material for most consumer electronics because it offers solid performance at a low cost.
2. Copper: The Performance Powerhouse
Thermal Conductivity: Excellent (around 385 W/m·K – nearly double that of aluminum)
Key Advantages:
- Superior heat transfer – ideal for quickly pulling heat away from critical components.
- Used in high-performance environments like gaming PCs, servers, and industrial machines.
Trade-offs:
- Heavier than aluminum.
- It’s more expensive and harder to manufacture.
- Prone to oxidation unless coated or sealed.
Copper is often used in critical hotspots (e.g., baseplates or heat pipes) even in aluminum heat sinks, combining the strengths of both materials.
Other Materials: Pushing the Limits
- Graphite – It’s very light and can conduct heat well in certain directions, making it ideal for small or portable devices like smartphones or tablets.
- Composites (e.g., copper-aluminum hybrids) – offer a middle ground between cost, weight, and performance.
Choosing the right heat sink material isn’t just about conductivity, it’s about the right balance of performance, weight, cost, and design. That’s why aluminum and copper remain the go-to choices: they consistently deliver effective, reliable thermal management across many industries.
Fascinating Fact #3: Design Isn’t Just About Looks: It’s Physics
Heat sinks might look simple, but they’re designed using science to remove heat from devices like computers and phones. Every part of a heat sink is there for a reason.
Thin metal fins give heat more space to escape, and they’re placed just right so air can flow through easily, either from a fan or just natural air movement. This helps carry the heat away.
The flat bottom of the heat sink must touch the hot part, like a CPU, really well so it can pull the heat away quickly. Some heat sinks use special pipes or thicker bases to spread heat more evenly.
Even the way the fins are arranged matters. Since heat rises, fins that point up help cool in systems without fans. In systems with fans, the fins are shaped to push heat out faster.
Bigger heat sinks cool more effectively, but designers must balance that with size and weight limits, especially in compact devices.
Heat sinks are all about smart design to keep electronics cool and working properly.
Fascinating Fact #4: Heat Sinks Go Beyond Electronics
Heat sinks are commonly associated with computers and electronics, but their use goes far beyond that.
Where Else Are Heat Sinks Used?
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): They help cool batteries, power inverters, and motor controllers, which are essential for performance and safety.
- LED Lighting: LEDs generate heat that must be managed to prevent damage and ensure long life. Heat sinks pull heat away to keep lights running efficiently.
- Industrial Equipment: Machines that run continuously can overheat. Heat sinks help maintain safe operating temperatures and prevent breakdowns.
- Solar Power Systems: Inverters and charge controllers in solar installations rely on heat sinks to stay cool while converting and managing energy.
- Medical Devices: Equipment like MRI machines, lasers, and imaging tools need stable temperatures for accurate, reliable operation.
- Telecom and Aerospace: Heat sinks manage heat in satellites, antennas, and base stations where high performance is required in extreme environments.
Heat sinks help many machines stay cool so they can work properly and safely in places like cars, hospitals, and solar farms.
Fascinating Fact #5: Innovation Is Heating Up
Heat sink technology is evolving quickly to keep up with smaller, faster, and more powerful devices. New materials, advanced designs, and modern manufacturing techniques are making heat sinks more efficient, compact, and effective. This ongoing innovation is crucial to help devices stay cool and perform better as technology advances.
Fascinating Fact #6: Heat Sink Efficiency Can Make or Break a Product
A heat sink is essential for keeping electronic devices cool. If it isn’t efficient, the device can overheat, leading to poor performance, system crashes, or permanent damage. This directly affects how well the product works, how long it lasts, and whether users are satisfied. In powerful or compact devices like smartphones, gaming PCs, or electric vehicles, even a small temperature issue can cause big problems. That’s why efficient heat sink design is critical to a product’s success.
Fascinating Fact #7: Sustainability Plays a Role Too
Heat sinks aren’t just made for cooling anymore, they’re also designed with the environment in mind. Manufacturers now often use recyclable materials like aluminum and energy-saving methods like 3D printing to produce them. Efficient heat sinks help devices stay cool and run better, which means they use less power, last longer and create less electronic waste. Smart heat sink design helps protect both technology and the planet.
Conclusion: Why Heat Sink Technology Matters More Than Ever
Heat sinks may be small and often hidden, but they’re powerful tools that keep our technology running smoothly. From smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and medical devices, heat sinks quietly manage heat to prevent overheating, system failure, and reduced performance.
Their design is rooted in science, with every material choice, shape, and feature carefully engineered for maximum cooling. Whether aluminum for its lightweight, copper for high performance, or innovative 3D-printed structures for space-saving solutions, heat sinks are evolving alongside modern tech demands.
Heat sinks use recyclable materials, save production energy, and extend device life, making them key to innovation, sustainability, and reliable electronics.





